- Logo Design by Brendan McCabe
vno

The first build tool for compiling and bundling Vue components in a Deno runtime environment




Features
- Parser
- Compiler
- Bundler
- Adapter
Overview
- Vue is an approachable javascript framework with an exciting ecosystem with remarkable versatility. Deno is a runtime environment intent on improving the shortcomings of node.js. We wanted to be able to leverage the Vue framework in a Deno runtime environment, and vno makes that possible.
How to use vno
- You can use the vno Command Line Interface to quickly create a new Vue project in a Deno runtime
- OR you can use the vno build method to compile an existing Vue file structure into a Deno-legible .js file
vno installation
- vno requires the use of Deno version 1.7 or above
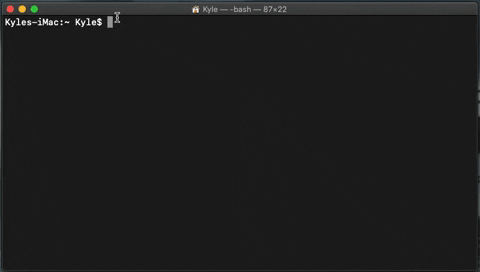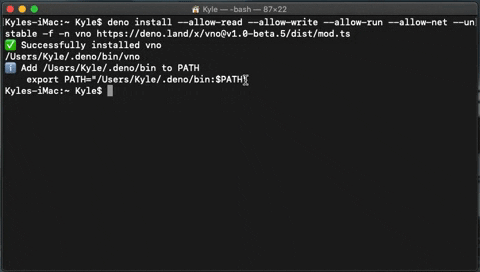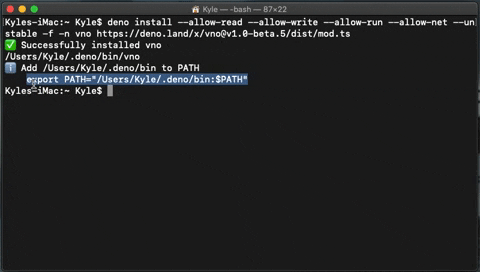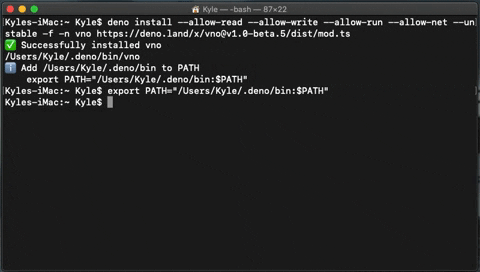
- run the following command in your terminal to install vno on your machine.
deno install --allow-net --unstable https://deno.land/x/vno/install/vno.tsDeno requires the
--allow-netpermission to run an installationThis feature, and many of the others used in vno are still considered "unstable" for Deno. Run the command with
--unstableto allow these resources to execute.The force flag
-fcan be used if you want to overwrite an existing copy of the moduleYou can name the module in your path with the name flag
-nor--name, 'vno' is the default name.If you have not already added Deno bin into your path, you will need to do so.
- Copy the export path your terminal returns and paste it into your terminal
a quick word about permissions
- Deno is secure by default, this means that explicit permissions are required for certain tasks.
- You can avoid responding to the permissions requests by flagging the installation script.
- Most of our module requires both read and write permissions
--allow-read&--allow-write - If you decide not to flag permissions at installation, you will be prompted in the terminal after executing a command.
- note: If you would like to avoid writing out the permissions altogether, you
can also use the
-Aor--allow-alltag
vno config
- vno.config.json should be in the root of your project
- following is a description of the object interface:
interface Config {
entry: string;
//entry is the path to root component's directory : i.e. './client/'
root: string;
//root is the filename of your root component : i.e. 'App'
vue?: 2 | 3;
//vue is the number 2 or 3 : 2 = vue v2.6.12 (default); 3 = vue v3.0.5
options?: {
port?: number;
//preferred port for the dev server : defaults to `3000`
title?: string;
//title of your project
hostname?: string;
//preferred host : defaults to `0.0.0.0`
};
}CLI
create a new project
- Project name will become the directory that holds your project (you must CD into project directory after running create command).
- If project name argument is omitted, then project will be created in current working directory.
vno create [project name]
- OR If you'd rather not install:
deno run --allow-read --allow-write --allow-net --unstable https://deno.land/x/vno/install/vno.ts create [project name]run a build on a project
- To invoke the build method and dynamically create bundled js and css files for your application type the following into the terminal:
vno buildOR
deno run --allow-read --allow-write --allow-net --unstable https://deno.land/x/vno/install/vno.ts build
It is important to know that as of now, scoped styling is not supported
run a simple dev server
- Running the dev server dynamically runs a new build and runs the application on a module hosted server
- Invoke the dev server like so:
vno run devOR
deno run --allow-read --allow-write --allow-net --unstable https://deno.land/x/vno/install/vno.ts run dev
vno as an API
initializing your application with the api
- You can import vno into your application with the following URL :
https://deno.land/x/vno/dist/mod.tsWith a vno.config.json, no argument is needed The API will search for the config and apply it to your application
import { Factory } from 'https://deno.land/x/vno/dist/mod.ts';
const vno = new Factory();
await vno.build();without a vno.config.json, you can input the object directly into the Factory instance
import { Factory } from 'https://deno.land/x/vno/dist/mod.ts';
const vno = Factory.create({
root: "App",
entry: "./"
vue: 3,
options: {
port: 3000
}
})
await vno.build();vno.build() will run a build on the entire application and compile it to a
"vno-build" directory as one javascript file and one css file.
accessing component object storage
- After running the build, parsed components are accessible inside the storage property on the Factory class.
vno.storage.get('App');the argument accepted by the get method for storage is the component filename